Stress Strain Curve Of Ceramic
ε dl l o σ e 3 where.
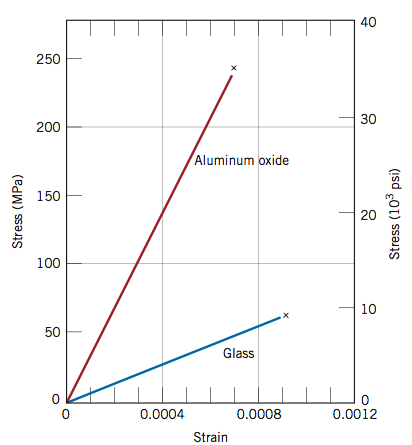
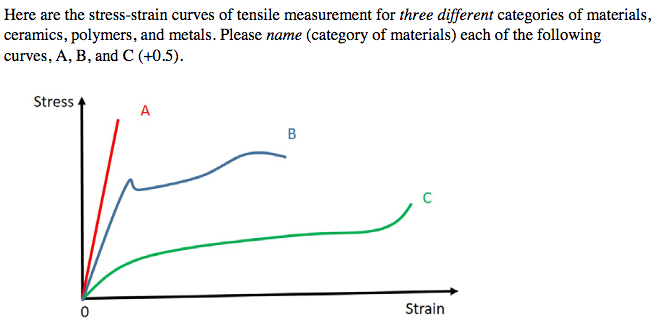
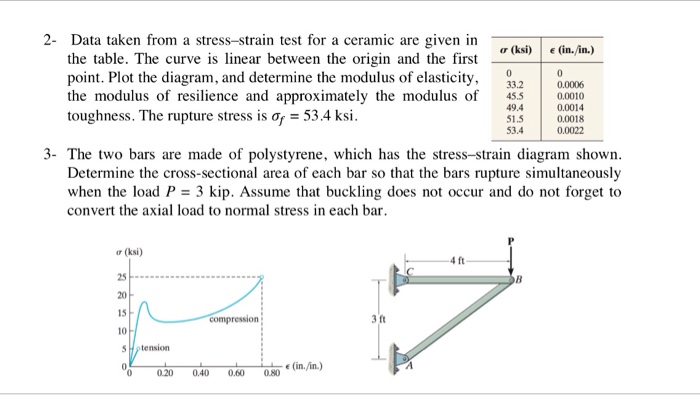
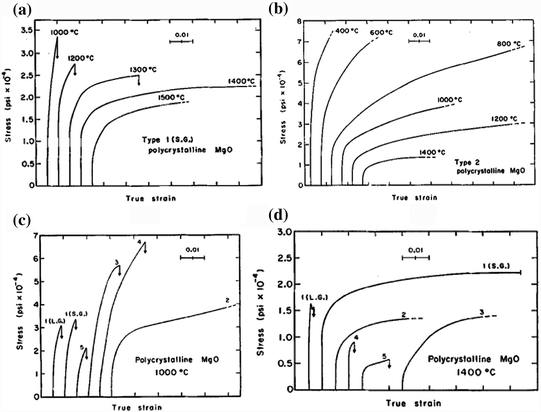
Stress strain curve of ceramic. Normal strain and can be expressed as. It was found that they behaved as elastic materials. For brittle ceramics a three point bending apparatus shown in the figure below is used determine the stress strain behavior and the measurement results are used to calculate an equivalent modulus of elasticity. Dl change of length m in.
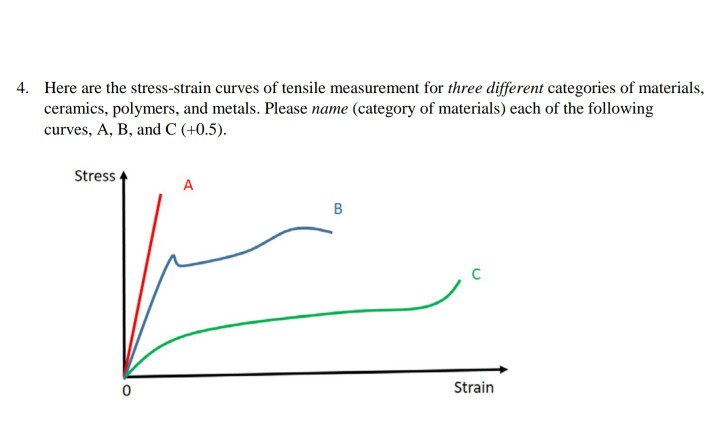
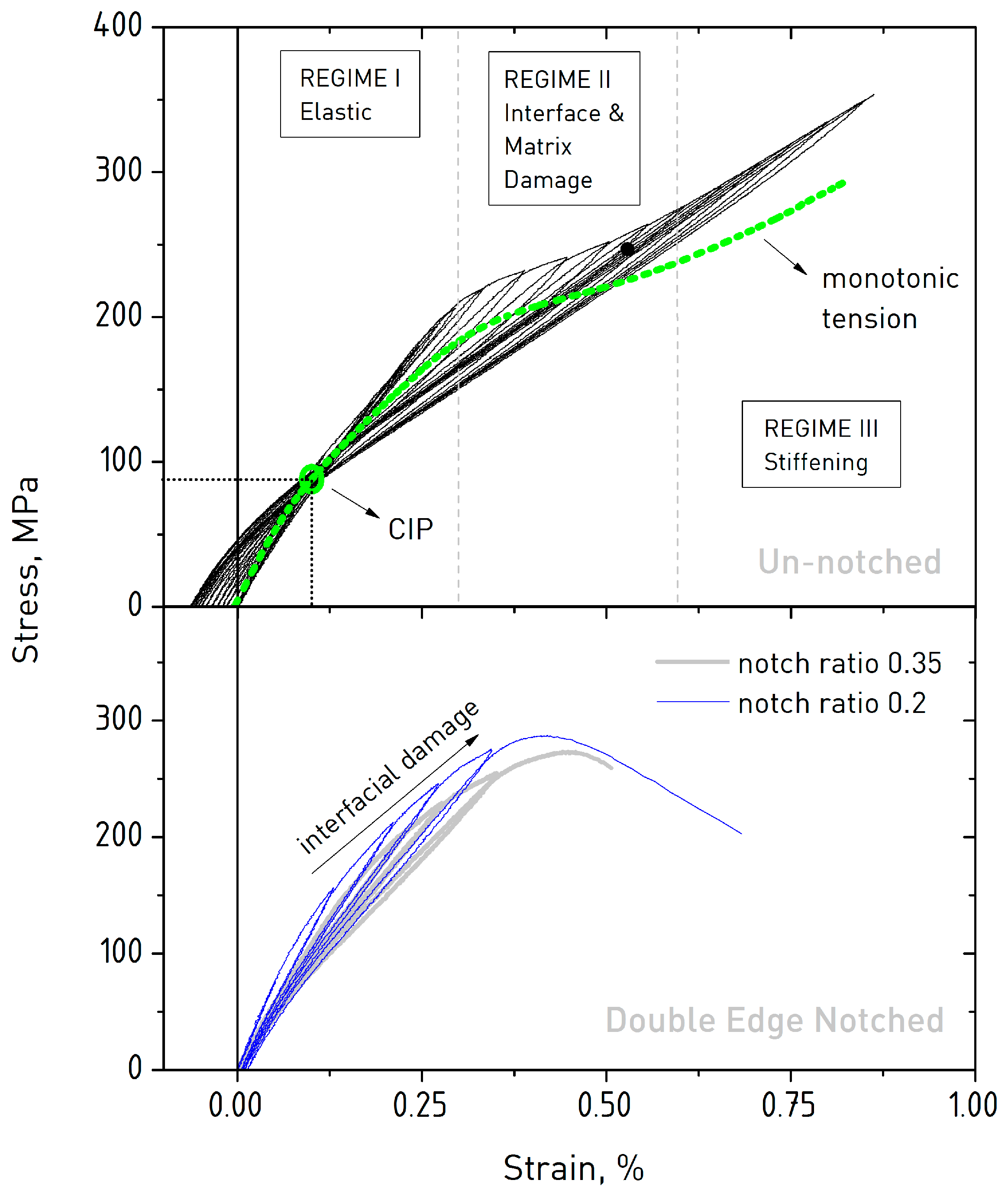
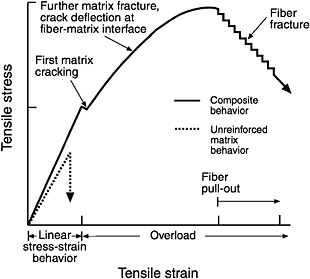
If the cyclic stress strain curve lies above below the monotonic stress strain curve the material cyclically hardens softens the cyclic fatigue behavior of ceramic materials has received. In engineering and materials science a stress strain curve for a material gives the relationship between stress and strain. Three point bending apparatus used determine stress strain behavior. Shear strain change in angle between two line segments originally perpendicular.
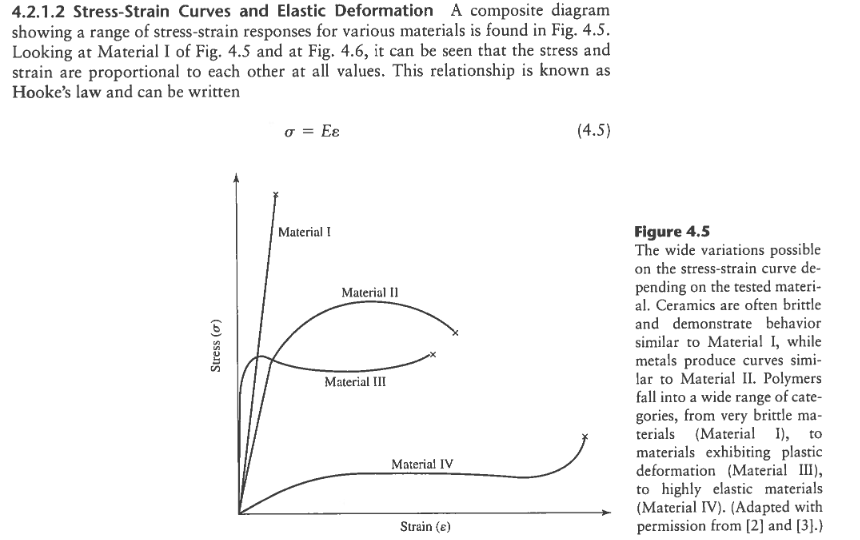
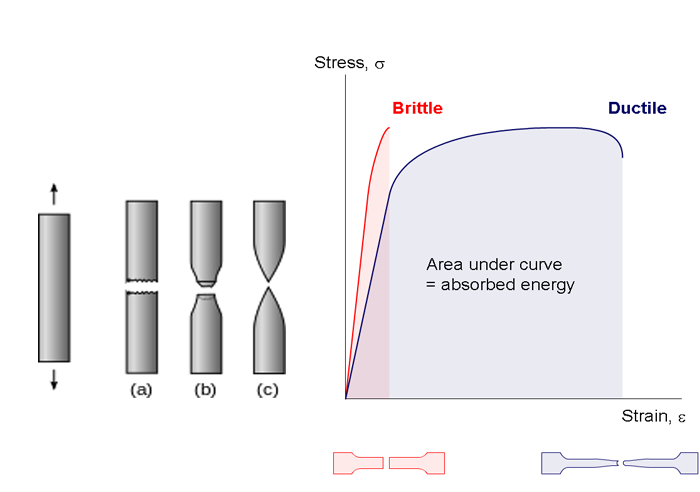
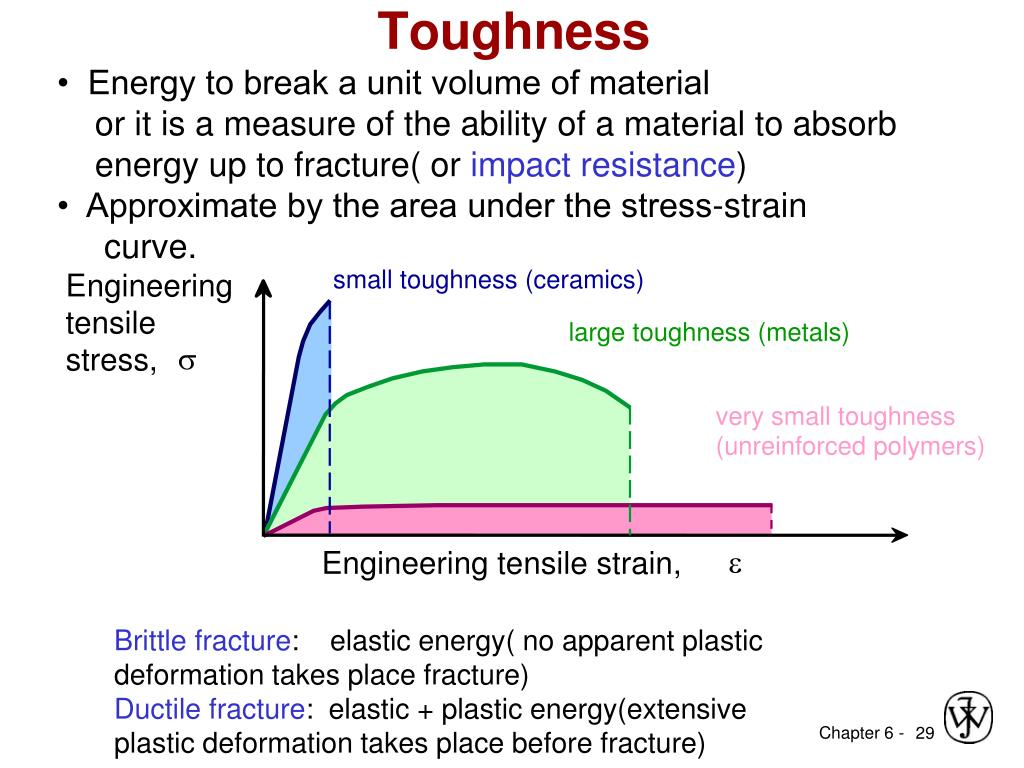
Strain is defined as deformation of a solid due to stress. Represents straightening of the crimped ligament fibrils. The zone where a material will return to its original shape for a given amount of stress toe region applies to a ligaments stress strain curve. The stress strain curve is approximated using the ramberg osgood equation which calculates the total strain elastic and plastic as a function of stress.
Abstract the electric strain gauge was used to study the deformation of several types of ceramic materials under stress. Stress vs strain curve. The hard fired materials exhibit straight line deformation to failure while the softer fired have a proportional elastic limit beyond which the stress strain curve deviates from a straight line. Where σ is the value of stress e is the elastic modulus of the material s ty is the tensile yield strength of the material and n is the strain hardening exponent of the material which.
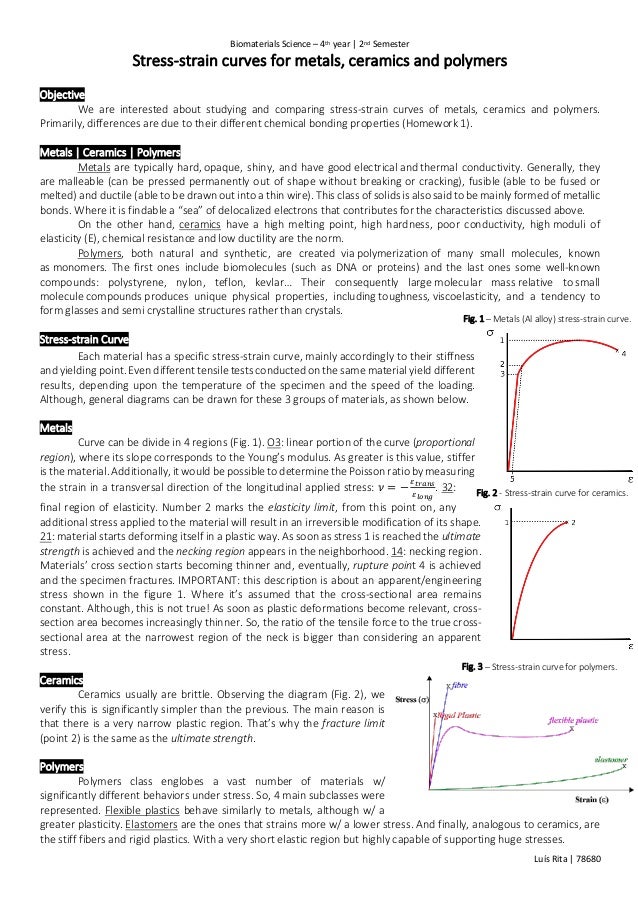
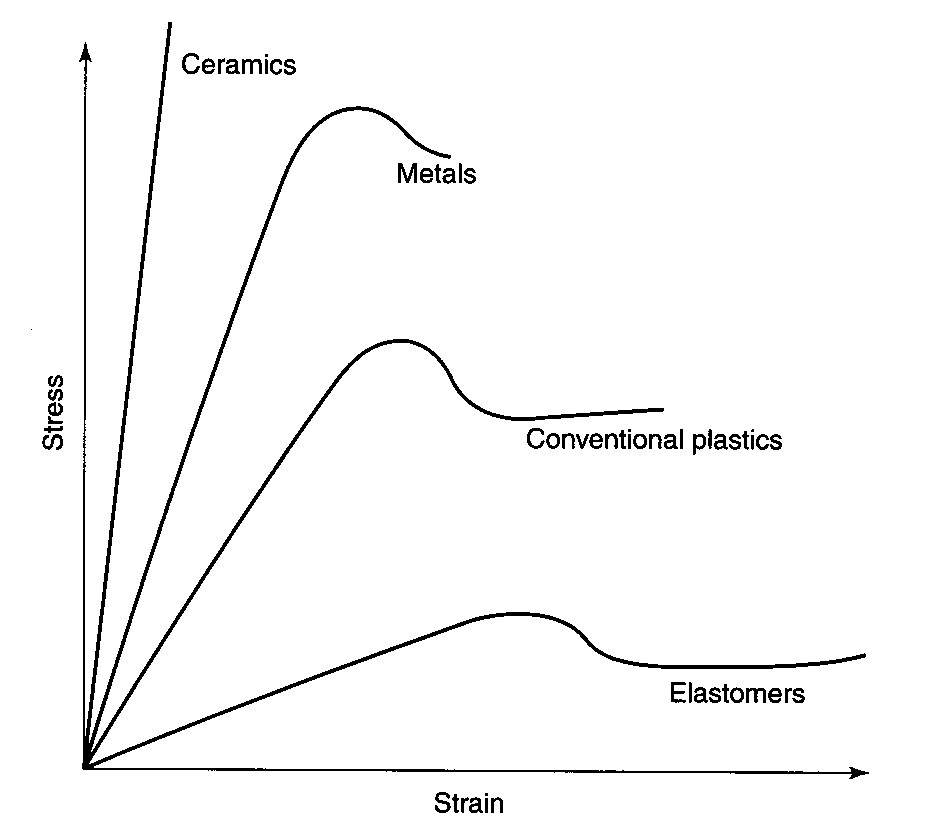
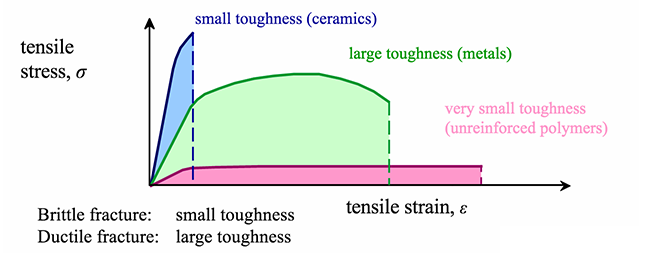
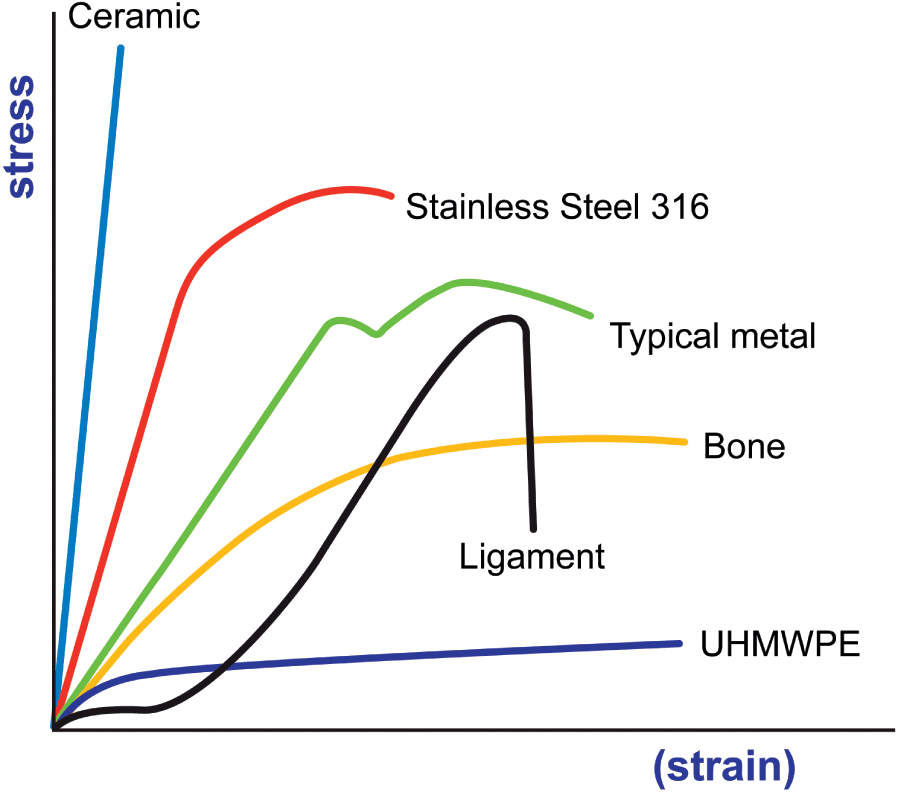
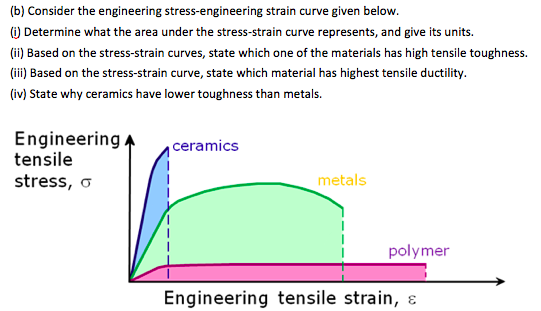
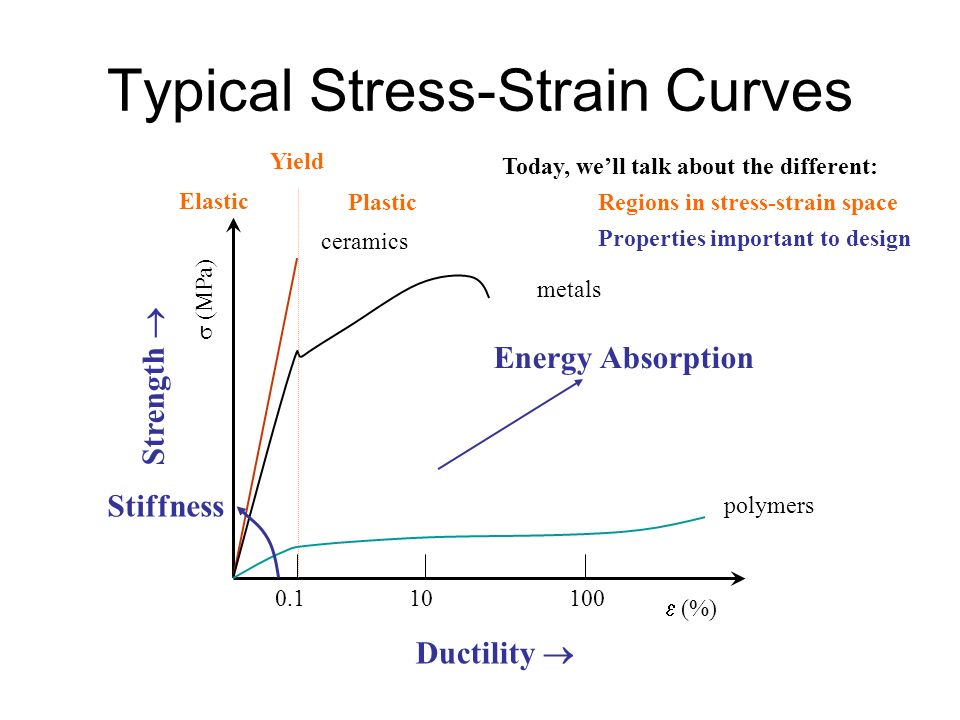
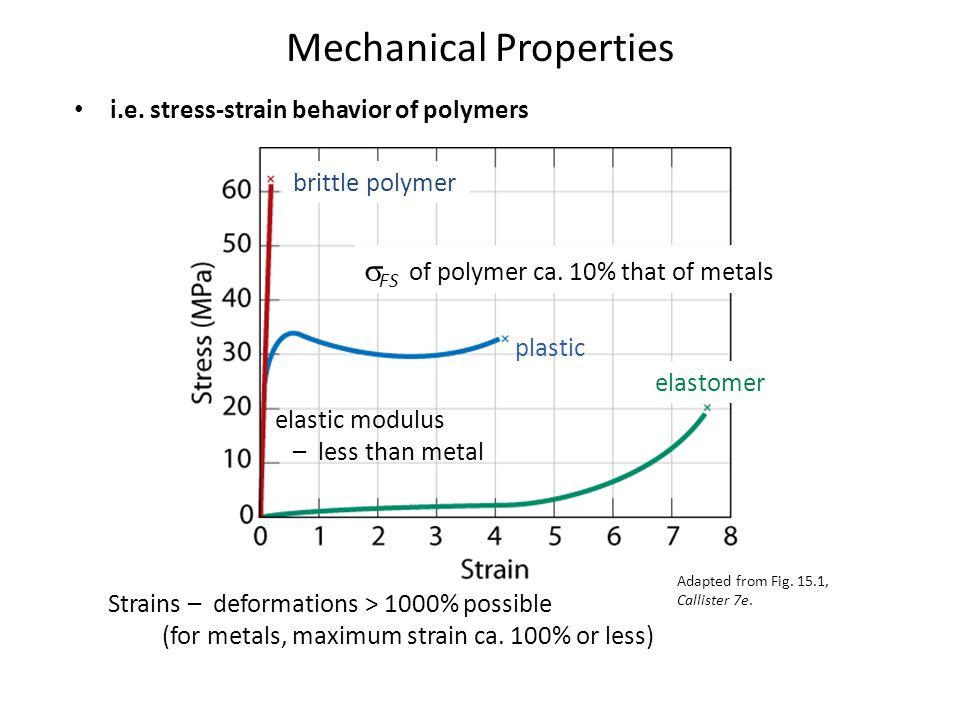
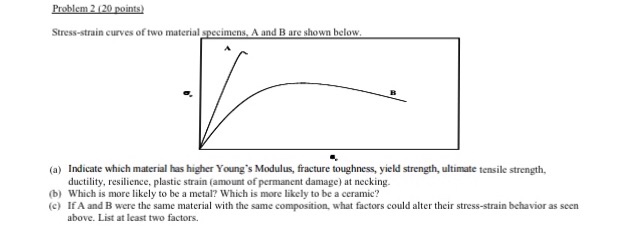
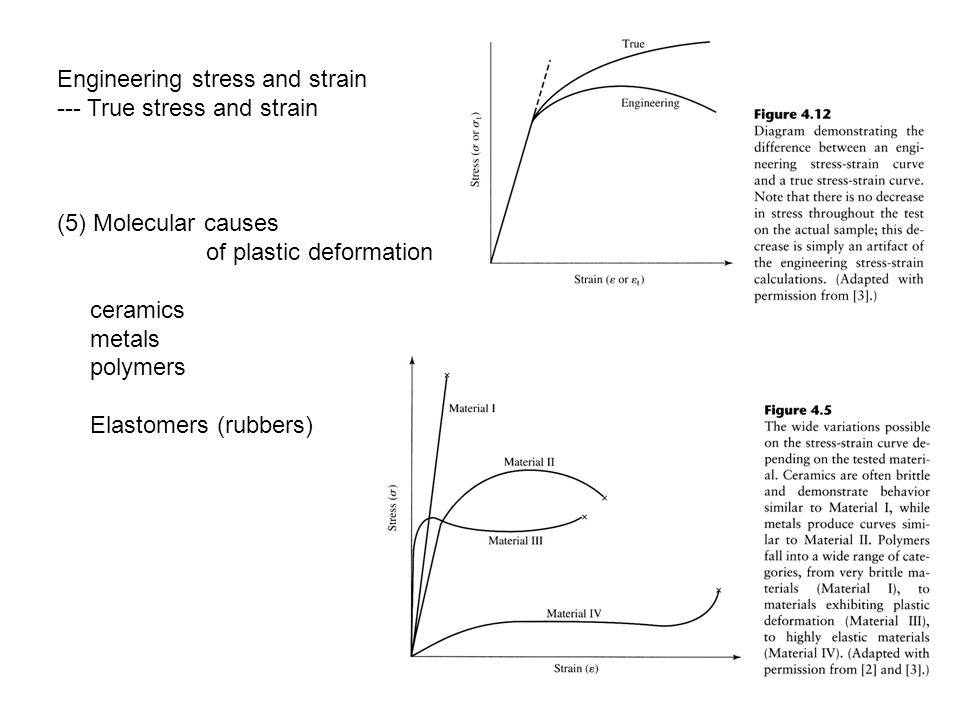
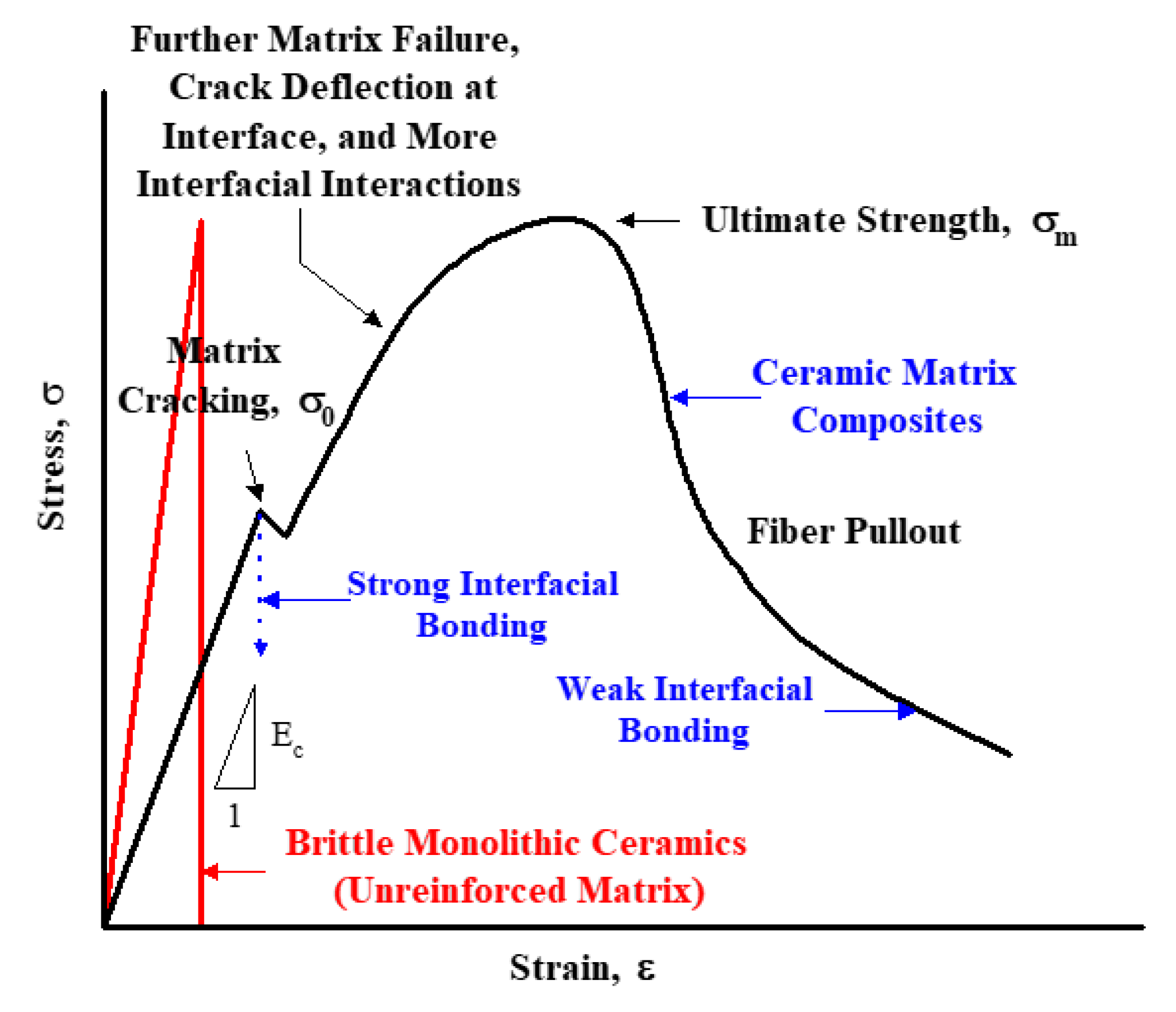
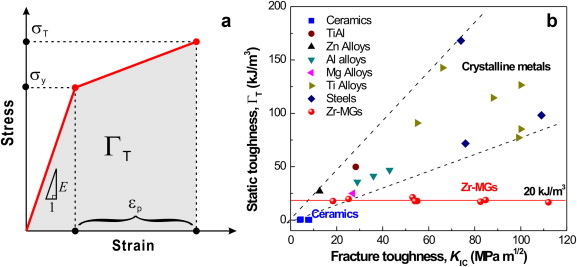
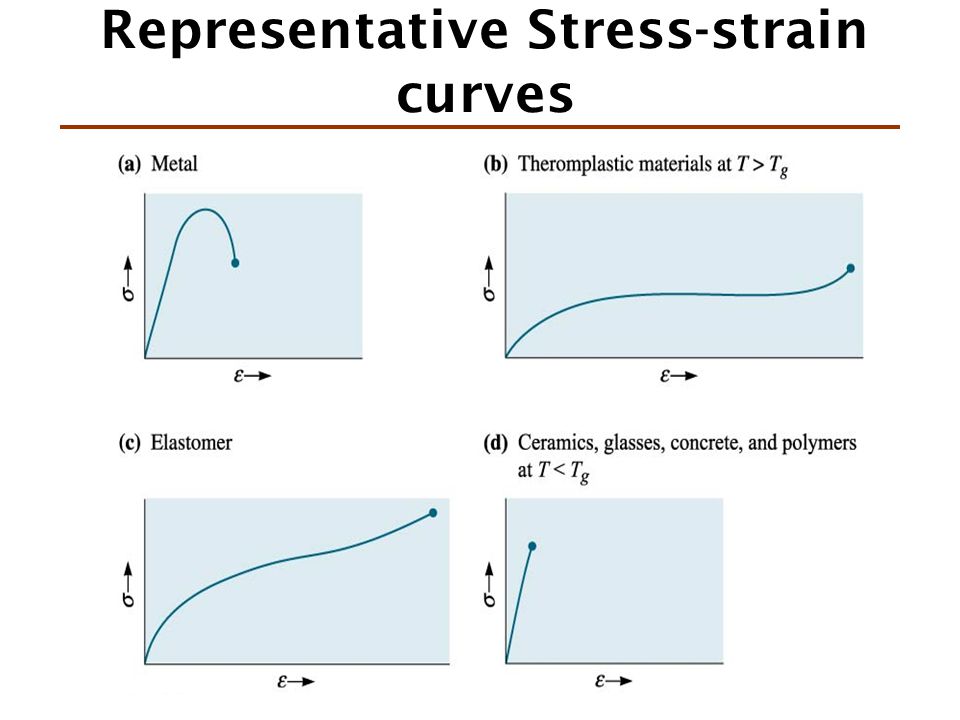
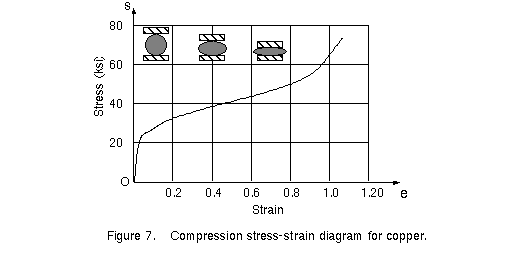
Stress strain curves for metals ceramics and polymers objective we are interested about studying and comparing stress strain curves of metals ceramics and polymers. Derived from axially loading an object and plotting the stress verses strain curve. Data indicate that. The hard fired materials exhibit straight line deformation to failure while the softer fired have a proportional elastic limit beyond which the stress strain curve deviates from a straight line.
It is obtained by gradually applying load to a test coupon and measuring the deformation from which the stress and strain can be determined see tensile testing. Data indicate that engineering formulas based on elastic materials may be applied to ceramic materials. Primarily differences are due to their different chemical bonding properties homework 1.